Individuals act as their own historians, suppressing some stories and emphasizing others. But at the scale of nations and cultures, and especially in this age of ubiquitous digital memory, it has become more difficult to forget. Building on questions about history and its uses, raised by exhibitions like Educating Architects: Four Courses by Kenneth Frampton and Besides,(...)
Johannes Grenzfurthner
12 April 2018
Come and Forget the Counterculture, with Johannes Grenzfurthner
Actions:
Description:
Individuals act as their own historians, suppressing some stories and emphasizing others. But at the scale of nations and cultures, and especially in this age of ubiquitous digital memory, it has become more difficult to forget. Building on questions about history and its uses, raised by exhibitions like Educating Architects: Four Courses by Kenneth Frampton and Besides,(...)
Johannes Grenzfurthner
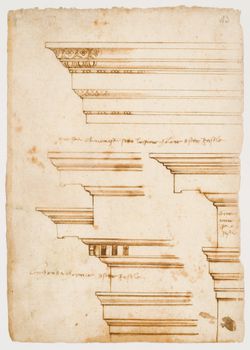
2016 Visiting Scholar Cara Rachele presents her research: This lecture investigates the explosion of detail drawings in the Renaissance. It connects the emergence of the detail in the sixteenth century as a canonical drawing type with the evocation of the material antique. The organic evolution of the detail drawing method can be seen in the sketchbooks of everyday(...)
11 August 2016, 6pm
Visiting Scholar Seminar: Cara Rachele
Actions:
Description:
2016 Visiting Scholar Cara Rachele presents her research: This lecture investigates the explosion of detail drawings in the Renaissance. It connects the emergence of the detail in the sixteenth century as a canonical drawing type with the evocation of the material antique. The organic evolution of the detail drawing method can be seen in the sketchbooks of everyday(...)
DR1974:0002:004:001-022
Description:
- This book contains 8 pages of text primarily describing projects by Charles Rohault de Fleury for the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. The text is followed by a lithograph after Lemaitre, which depicts the exterior of the "serres chaudes", and by 14 prints engraved/etched by Marlier depicting the buildings designed by Rohault de Fleury for the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle between 1833 and 1839. The "serres chaudes" are illustrated by 8 prints: interior perspectives, plans, elevations, sections and details of the prefabricated columns. Four prints are included for the Galerie de minéralogie et de géologie, the monkey house and the reservoirs - mostly elevations, plans and sections. Also included is a site plan of the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle and one print of comparative examples - mostly plans, sections and details - of English "serres chaudes", including the Warm House and the Temperate House at the Colosseum in London, the Temperate House at the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew, Camellia House and Palm House at Loddiges Nursery in Hackney, and a glasshouse with a semidome, also in Hackney.
architecture, landscape architecture, engineering
published 1837
MUSÉUM / D'HISTOIRE NATURELLE / SERRES CHAUDES, / GALERIE DE MINÉRALOGIE, / ETC. ETC. / PAR. CH. ROHAULT FILS, / ARCHITECTE DU MUSÉUM, ANCIEN ÉLEVE DE L'ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE
Actions:
DR1974:0002:004:001-022
Description:
- This book contains 8 pages of text primarily describing projects by Charles Rohault de Fleury for the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. The text is followed by a lithograph after Lemaitre, which depicts the exterior of the "serres chaudes", and by 14 prints engraved/etched by Marlier depicting the buildings designed by Rohault de Fleury for the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle between 1833 and 1839. The "serres chaudes" are illustrated by 8 prints: interior perspectives, plans, elevations, sections and details of the prefabricated columns. Four prints are included for the Galerie de minéralogie et de géologie, the monkey house and the reservoirs - mostly elevations, plans and sections. Also included is a site plan of the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle and one print of comparative examples - mostly plans, sections and details - of English "serres chaudes", including the Warm House and the Temperate House at the Colosseum in London, the Temperate House at the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew, Camellia House and Palm House at Loddiges Nursery in Hackney, and a glasshouse with a semidome, also in Hackney.
architecture, landscape architecture, engineering
Our Visiting Scholar Nader Vossoughian talks about informal urban planning as seen through the history of encyclopedism, using the Whole Earth Catalog as a case study. Click here for the Facebook event.
Shaughnessy House
Presented in English Keyword(s):
Nader Vossoughian, visiting scholar, seminar
9 August 2012 , 6PM
Visiting Scholar Seminar: Nader Vossoughian
Actions:
Description:
Our Visiting Scholar Nader Vossoughian talks about informal urban planning as seen through the history of encyclopedism, using the Whole Earth Catalog as a case study. Click here for the Facebook event.
Shaughnessy House
Presented in English Keyword(s):
Nader Vossoughian, visiting scholar, seminar
Meetings and News Releases
ARCH203210
Description:
Publications et extraits de publications dans lesquels fut publié le communiqué de presse invitant la population à participer à la levée de fonds (1966-1967); texte de Przygoda sur l'histoire des Polonais adressé au Congrès Canadien polonais (1966); brouillon du texte de la circulaire annoté; correspondance (1966); minutes du comité du monument (1966); coupures de journaux et publications (1966); "mailing list for news releases, 1966"; communiqué de presse (1966); notes manuscrites.
avril 1966 à juin 1967
Meetings and News Releases
Actions:
ARCH203210
Description:
Publications et extraits de publications dans lesquels fut publié le communiqué de presse invitant la population à participer à la levée de fonds (1966-1967); texte de Przygoda sur l'histoire des Polonais adressé au Congrès Canadien polonais (1966); brouillon du texte de la circulaire annoté; correspondance (1966); minutes du comité du monument (1966); coupures de journaux et publications (1966); "mailing list for news releases, 1966"; communiqué de presse (1966); notes manuscrites.
avril 1966 à juin 1967
Mrinalini Rajagopalan traces the history of the Red Fort in Delhi from its destruction by the British in 1857 to their later efforts to preserve and protect the same structure. Click here for a listing of the rest of this summer’s seminars.
Shaughnessy House
8 July 2010
Visiting Scholar Seminar: Mrinalini Rajagopalan
Actions:
Description:
Mrinalini Rajagopalan traces the history of the Red Fort in Delhi from its destruction by the British in 1857 to their later efforts to preserve and protect the same structure. Click here for a listing of the rest of this summer’s seminars.
Shaughnessy House
In 1982, the CCA organized its first exhibition, Photography and Architecture: 1839–1939, prior to the construction of the CCA’s current building. The exhibition was shown in Galerie Lempertz Contempora in Cologne (1982), the Art Institute of Chicago (1983), the Cooper-Hewitt National Design Museum in New York (1983), Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris (1984), and the(...)
15 September 1982 to 16 October 1982
Photography and Architecture: 1839–1939
Actions:
Description:
In 1982, the CCA organized its first exhibition, Photography and Architecture: 1839–1939, prior to the construction of the CCA’s current building. The exhibition was shown in Galerie Lempertz Contempora in Cologne (1982), the Art Institute of Chicago (1983), the Cooper-Hewitt National Design Museum in New York (1983), Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris (1984), and the(...)
When Gordon Matta-Clark assembled the titles to and documentation of a dozen-odd small, vacant parcels of New York property between 1974 and 1977 (later assembled and exhibited as Reality Properties: Fake Estates in 1992), it was with no well-formed agenda—other than his view that the availability of vacant and underutilized parcels [was] a direct reminder of the fallacy(...)
Paul Desmarais Theatre
22 September 2016, 6pm
Nicholas de Monchaux: Local Code
Actions:
Description:
When Gordon Matta-Clark assembled the titles to and documentation of a dozen-odd small, vacant parcels of New York property between 1974 and 1977 (later assembled and exhibited as Reality Properties: Fake Estates in 1992), it was with no well-formed agenda—other than his view that the availability of vacant and underutilized parcels [was] a direct reminder of the fallacy(...)
Paul Desmarais Theatre
Architectural historian Barbara Penner traces the evolution of Niagara Falls – from its 19th-century honeymoon tourism to its state of post-industrial kitsch to its recent rebirth as a honeymoon destination. The photographer Alec Soth, whose work is the starting point for this lecture, compellingly portrays a ruined post-industrial landscape of love in his series Niagara(...)
Paul Desmarais Theatre
23 April 2009
Learning from... Niagara Falls
Actions:
Description:
Architectural historian Barbara Penner traces the evolution of Niagara Falls – from its 19th-century honeymoon tourism to its state of post-industrial kitsch to its recent rebirth as a honeymoon destination. The photographer Alec Soth, whose work is the starting point for this lecture, compellingly portrays a ruined post-industrial landscape of love in his series Niagara(...)
Paul Desmarais Theatre
articles
Where Was Not Modernism?
Where Was Not Modernism?
Ikem Stanley Okoye redefines the origins of African modernism
Actions: