DR1996:0004
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture, urbanisme
1952-1953
Bird's-eye perspective for Village Polychrome, near Biot, France
Actions:
DR1996:0004
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture, urbanisme
DR1996:0005
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture, urbanisme
1952-1953
Bird's-eye perspective for Village Polychrome, near Biot, France
Actions:
DR1996:0005
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture, urbanisme
DR1996:0006
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture, urbanisme
1952-1953
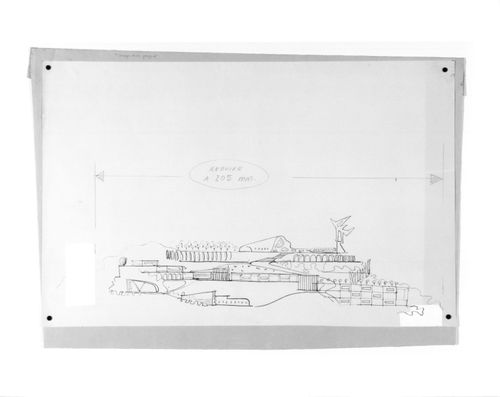
Site elevation for Village Polychrome, near Biot, France
Actions:
DR1996:0006
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture, urbanisme
DR1996:0007
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture, urbanisme
1952-1953
Site elevation for Village Polychrome, near Biot, France
Actions:
DR1996:0007
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture, urbanisme
DR1996:0008
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture
1952-1953
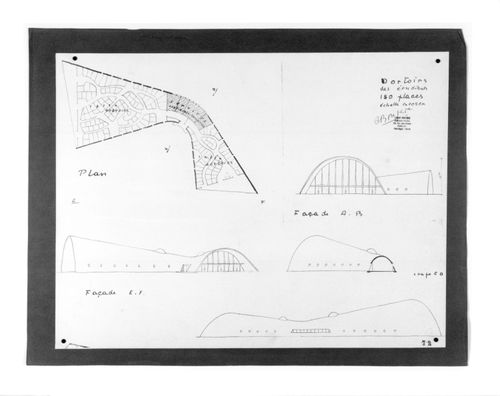
Plan, elevations and a section for the dormitory, Village Polychrome, near Biot, France
Actions:
DR1996:0008
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture
DR1996:0009
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture
1952-1953
Perspective for a villa with three workshops, Village Polychrome, near Biot, France
Actions:
DR1996:0009
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture
DR1996:0010
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture
1952-1953
Perspective for a guest villa showing the terrace and the principal and lateral façades, Village Polychrome, near Biot, France
Actions:
DR1996:0010
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture
DR1996:0012
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture
May 1953
Specifications for Village Polychrome, near Biot, France
Actions:
DR1996:0012
Description:
- Two groups of four pastel drawings were originally produced in connection with the Village Polychrome project. The architect André Bruyère had retained one group, while the other was given to the patron and client, Francisco de Assis Chateaubriand Bandeira de Melo, who then donated it to the Sao Paolo Museum of Modern Art. Bruyère subsequently gave one of the four drawings in his group to a friend. The three remaining drawings from Bruyère's group are in the CCA Prints and Drawings collection (DR1996:0001 - DR1996:0003) ("Projet de Village Polychrome, Biot, France").
architecture
Projet
AP143.S4.D108
Description:
The project series documents the executed project for Cites of Artificial Excavation, Madrid, Spain. Material in was produced between 1994 and 1995. In 1993, the CCA invited Peter Eisenman to design an installation for the exhibition 'Cities of Artificial Excavation: The Work of Peter Eisenman, 1978-1988'. The exhibition was presented at the CCA from 2 March to 29 May 1994. The drawings and models in this project series document the development of Eisenman's installation design from late 1993 through March 1994, as well as the various processes used by the architect in his investigation of the 'Cities of Artificial Excavation'. Eisenman uses a computer to superimpose, distort and multiply a Greek cross, while simultaneously modifying its plan and section. The computer enables the architect to generate geometric figures that are extremely difficult to produce by traditional means. It also constitutes a new phase in Eisenman's research into the depersonalization of the creative process, a central concern of his 'Cities of Artificial Excavation' (1978-1988). The Greek cross was one of the elements of the grid developed for the 'Museum of Artifical Excavation', and part of the project he submitted for the Internationale Bauausstellung in Berlin (1980-1986). The project series contains material by Eisenman's office including material for schemes A and B, the first and second proposals for the installation, as well as material for the exhibition installation. Material for scheme A includes conceptual drawings (DR1994:0030:001-005), hardline design development drawings (DR1994:0030:006-011), design development computer-aided drawings (DR1994:0030:012-027), and fully developed drawings (DR1994:0030:028-034). Material for scheme B, a design which is closer to the final project, includes hardline drawings (DR1994:0030:035-044) and computer-aided drawings (DR1994:0030:045-069). Material for the exhibition installation includes: computer-aided drawings (DR1994:0030:070-196) which were generated to construct models for the installation, notably a preliminary model (DR1994:0035) and the final model (DR1994:0036) which was used for planning the exhibition layout; hardline drawings which are the final drawings for the installation (DR1994:0030:262-265); a preliminary exhibition layout (DR1994:0030:280); and Iris colour prints of computer-aided conceptual axonometrics (DR1994:0030:281-282). Three working models show different stages of the design development (DR1994:0031 - DR1994:0034). Also included are photographs of the completed installation by Richard Pare (DR1994:0037:001-028), fragments of the installation preserved after its demolition (DR1994:0038:001-0028), and paint samples (DR1994:0038:035-037). The project series contains design development drawings, working drawings, photographic materials, publication drawings, reference drawings, textual records, and models.
1994-1995
Cities of Artificial Excavation, Madrid
Actions:
AP143.S4.D108
Description:
The project series documents the executed project for Cites of Artificial Excavation, Madrid, Spain. Material in was produced between 1994 and 1995. In 1993, the CCA invited Peter Eisenman to design an installation for the exhibition 'Cities of Artificial Excavation: The Work of Peter Eisenman, 1978-1988'. The exhibition was presented at the CCA from 2 March to 29 May 1994. The drawings and models in this project series document the development of Eisenman's installation design from late 1993 through March 1994, as well as the various processes used by the architect in his investigation of the 'Cities of Artificial Excavation'. Eisenman uses a computer to superimpose, distort and multiply a Greek cross, while simultaneously modifying its plan and section. The computer enables the architect to generate geometric figures that are extremely difficult to produce by traditional means. It also constitutes a new phase in Eisenman's research into the depersonalization of the creative process, a central concern of his 'Cities of Artificial Excavation' (1978-1988). The Greek cross was one of the elements of the grid developed for the 'Museum of Artifical Excavation', and part of the project he submitted for the Internationale Bauausstellung in Berlin (1980-1986). The project series contains material by Eisenman's office including material for schemes A and B, the first and second proposals for the installation, as well as material for the exhibition installation. Material for scheme A includes conceptual drawings (DR1994:0030:001-005), hardline design development drawings (DR1994:0030:006-011), design development computer-aided drawings (DR1994:0030:012-027), and fully developed drawings (DR1994:0030:028-034). Material for scheme B, a design which is closer to the final project, includes hardline drawings (DR1994:0030:035-044) and computer-aided drawings (DR1994:0030:045-069). Material for the exhibition installation includes: computer-aided drawings (DR1994:0030:070-196) which were generated to construct models for the installation, notably a preliminary model (DR1994:0035) and the final model (DR1994:0036) which was used for planning the exhibition layout; hardline drawings which are the final drawings for the installation (DR1994:0030:262-265); a preliminary exhibition layout (DR1994:0030:280); and Iris colour prints of computer-aided conceptual axonometrics (DR1994:0030:281-282). Three working models show different stages of the design development (DR1994:0031 - DR1994:0034). Also included are photographs of the completed installation by Richard Pare (DR1994:0037:001-028), fragments of the installation preserved after its demolition (DR1994:0038:001-0028), and paint samples (DR1994:0038:035-037). The project series contains design development drawings, working drawings, photographic materials, publication drawings, reference drawings, textual records, and models.
File 108
1994-1995
Sous-série
AP018.S1.1980.PR09.SS1
Description:
This project series documents the design and construction of an office building for Marathon Realty in Toronto at the corner of York and Front Streets from 1980-1983. The office identified the project number as 8009. The project consisted of two nineteen storey towers with stainless steel and glass exteriors connected by a glass atrium on each floor. Owned and commissioned by Marathon Realty, the majority of the building’s space was designed for rental. Due to this, the design was highly modular with no interior walls on most floors. Each floor was approximately 18,000 square feet. The ground floor consisted of a lobby, a bank and a restaurant. At the beginning of this project, the project was named Marathon Realty Office Building, Front and York Streets. Soon after, the office building became known as University Place, which it is often referred to as in these materials. Eventually, the building would become the headquarters of CitiBank and renamed Citigroup Place. The project is recorded through drawings, photographs, textual records and other materials dating from 1980-1987. The majority of the drawings are located within the textual records and show the design of building details. Other drawings include site surveys, design development drawings, presentation drawings, and construction drawings. The photographs show construction progress, tests, models, and the finished project. The textual records contain the project proposal, contracts, client and contractor correspondence, inter-office memos, meeting minutes, financial records, change orders, supplementary instructions, specifications, detail planning, artist’s portfolios for the building’s art competition, site inspection reports, and schedules. File AP018.S1.1980.PR09.004 contains an index to the textual records, which was created by the office. The CCA also holds materials for a subproject under this project series, which document the installation of signs to the top of the building after the building's construction (AP018.S1.1980.PR09.SS1). Subproject materials are viewed separately from the project due to the different project numbers originally assigned by the office.
1980-1987
University Place Building, Front and York Streets, Toronto (1980-1987)
Actions:
AP018.S1.1980.PR09.SS1
Description:
This project series documents the design and construction of an office building for Marathon Realty in Toronto at the corner of York and Front Streets from 1980-1983. The office identified the project number as 8009. The project consisted of two nineteen storey towers with stainless steel and glass exteriors connected by a glass atrium on each floor. Owned and commissioned by Marathon Realty, the majority of the building’s space was designed for rental. Due to this, the design was highly modular with no interior walls on most floors. Each floor was approximately 18,000 square feet. The ground floor consisted of a lobby, a bank and a restaurant. At the beginning of this project, the project was named Marathon Realty Office Building, Front and York Streets. Soon after, the office building became known as University Place, which it is often referred to as in these materials. Eventually, the building would become the headquarters of CitiBank and renamed Citigroup Place. The project is recorded through drawings, photographs, textual records and other materials dating from 1980-1987. The majority of the drawings are located within the textual records and show the design of building details. Other drawings include site surveys, design development drawings, presentation drawings, and construction drawings. The photographs show construction progress, tests, models, and the finished project. The textual records contain the project proposal, contracts, client and contractor correspondence, inter-office memos, meeting minutes, financial records, change orders, supplementary instructions, specifications, detail planning, artist’s portfolios for the building’s art competition, site inspection reports, and schedules. File AP018.S1.1980.PR09.004 contains an index to the textual records, which was created by the office. The CCA also holds materials for a subproject under this project series, which document the installation of signs to the top of the building after the building's construction (AP018.S1.1980.PR09.SS1). Subproject materials are viewed separately from the project due to the different project numbers originally assigned by the office.
Project
1980-1987