articles
Exhibition Machines, Ghosts
David Van Severen, Greg Barton, Iñaki Ábalos, Juan Herreros, Kersten Geers, Ábalos&Herreros
5 February 2020
articles
machine learning, machine learning tool, architectural drawings, trees, AI, artificial intelligence, architectural history, protocols, toolkit, research methods
10 July 2023
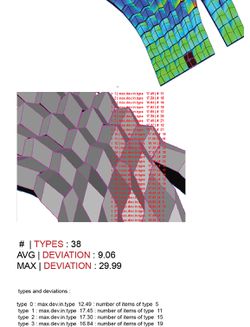
Learning from Machine Learning
Sylvia Lavin on designer trees and architectural historiographies of the digital
Actions:
That digital tools have changed the very nature of designing and making buildings is unquestioned. Yet formal innovation and ingenuity—and the technical competence needed to achieve those ends—are not merely a function of the virtuosity of form-making. Rather, they also make evident the dramatic impact that digital capabilities have on the roles, responsibility, and(...)
Paul Desmarais Theatre
20 October 2016, 6pm
Sound Advice and Clear Drawings: Design and Computation in the Second Machine Age
Actions:
Description:
That digital tools have changed the very nature of designing and making buildings is unquestioned. Yet formal innovation and ingenuity—and the technical competence needed to achieve those ends—are not merely a function of the virtuosity of form-making. Rather, they also make evident the dramatic impact that digital capabilities have on the roles, responsibility, and(...)
Paul Desmarais Theatre
Media and Machines marks the second phase of the research project initiated with the 2013 exhibition Archaeology of the Digital. This initiative investigates how architecture engaged with digital technology from the 1980s until the turn of the century. The first exhibition identified the earliest practices looking to computation as a design medium that could serve(...)
Main galleries
21 May 2014 to 5 October 2014
Archaeology of the Digital: Media and Machines
Actions:
Description:
Media and Machines marks the second phase of the research project initiated with the 2013 exhibition Archaeology of the Digital. This initiative investigates how architecture engaged with digital technology from the 1980s until the turn of the century. The first exhibition identified the earliest practices looking to computation as a design medium that could serve(...)
Main galleries
Machine à ecrire
ARCH257858
Description:
Étui, machine à écrire et clé (cassée).
1900s
1900s
photographs
Machine Tools
PH1989:0262.02:015
engineering
1851
photographs
1851
engineering
photographs
PH1989:0262.02:009
Description:
Photograph of machine called 'L'Épurateur' for opening and cleaning cotton.
engineering
1851
"Epurator" Machine for Cleaning
Actions:
PH1989:0262.02:009
Description:
Photograph of machine called 'L'Épurateur' for opening and cleaning cotton.
photographs
1851
engineering
Project
AP012.S1.SS6.D3
Description:
Le dossier est constitué d'un dessin relié au projet "Tony" Leather-Cutting Machine.
s.d.
"Tony" Leather-Cutting Machine
Actions:
AP012.S1.SS6.D3
Description:
Le dossier est constitué d'un dessin relié au projet "Tony" Leather-Cutting Machine.
Dossier 3
s.d.
Series
AP115.S1
Description:
Cette série porte sur le travail de documentation photographique de Robert Duchesnay d'un des exemples construit du Dymaxion Dwelling Machine, à Wichita, Kansas, aux États-Unis. Le Dymaxion Dwelling Machine, concept conçu par Buckminster Fuller et considéré comme le précurseur du dôme géodésique, visait a créer un mode d'habitation donnant un maximun d'espace pour un minimum de coût et de matériaux. L'exemple du Wichita House est conçu par Fuller en 1945-1946. "L'apparence de cette machine à habiter ressemble quelque peu à une soucoupe volante. Avec sa peau externe en aluminium et ses fenêtres en plexiglass, elle offre un surface élégante et profilée, tout en renferman un espace au sol de 1100 pieds carrées." [1] Le Dymaxion Dwelling Machine est abandonné en 1970, pour être finalement acquise en 1990 par le Henry Ford Museum à Detroit, au Michigan. La structure est démantelé la même année avec l'aide d'un ancien collaborateur de Buckminster Fuller, Jay Baldwin. Le Dymaxion Dwelling Machine est toujours visible au Ford Museum. La série contient des photographies de la Wichita House avant et durant le démantèlement, brochures et feuillets du Wichita Art Museum présentant l'exposition de Robert Duchesnay sur le bâtiment, correspondance reçue par Duchesnay sur son projet de documentation des dômes géodésiques de Buckminster Fuller, et coupures de presse sur le Dymaxion Dwelling Machine et le démantèlement de la Wichita House. [1] Robert Duchesnay, "Dymaxion Dwelling Machine", 2022, https://robertduchesnay.com/fr/dymaxion-fr/ (page consultée 27 février 2023).
1990-1992
Dymaxion Dwelling Machine, Wichita, Kansas
Actions:
AP115.S1
Description:
Cette série porte sur le travail de documentation photographique de Robert Duchesnay d'un des exemples construit du Dymaxion Dwelling Machine, à Wichita, Kansas, aux États-Unis. Le Dymaxion Dwelling Machine, concept conçu par Buckminster Fuller et considéré comme le précurseur du dôme géodésique, visait a créer un mode d'habitation donnant un maximun d'espace pour un minimum de coût et de matériaux. L'exemple du Wichita House est conçu par Fuller en 1945-1946. "L'apparence de cette machine à habiter ressemble quelque peu à une soucoupe volante. Avec sa peau externe en aluminium et ses fenêtres en plexiglass, elle offre un surface élégante et profilée, tout en renferman un espace au sol de 1100 pieds carrées." [1] Le Dymaxion Dwelling Machine est abandonné en 1970, pour être finalement acquise en 1990 par le Henry Ford Museum à Detroit, au Michigan. La structure est démantelé la même année avec l'aide d'un ancien collaborateur de Buckminster Fuller, Jay Baldwin. Le Dymaxion Dwelling Machine est toujours visible au Ford Museum. La série contient des photographies de la Wichita House avant et durant le démantèlement, brochures et feuillets du Wichita Art Museum présentant l'exposition de Robert Duchesnay sur le bâtiment, correspondance reçue par Duchesnay sur son projet de documentation des dômes géodésiques de Buckminster Fuller, et coupures de presse sur le Dymaxion Dwelling Machine et le démantèlement de la Wichita House. [1] Robert Duchesnay, "Dymaxion Dwelling Machine", 2022, https://robertduchesnay.com/fr/dymaxion-fr/ (page consultée 27 février 2023).
Série
1990-1992