Miroirs / Mirrors
Miroirs/ Mirrors prend forme à travers un dialogue indirect avec l’exposition L’histoire, par ailleurs: Go Hasegawa, Kersten Geers, David Van Severen, qui prend racine dans les références et les résonnances partagées entre les travaux de deux pratiques contemporaines mises en présence de l’histoire. Alors que L’histoire, par ailleurs se fonde sur limpression que lon a du(...)
Vitrines
22 juin 2017 au 14 janvier 2018
Miroirs / Mirrors
Actions:
Description:
Miroirs/ Mirrors prend forme à travers un dialogue indirect avec l’exposition L’histoire, par ailleurs: Go Hasegawa, Kersten Geers, David Van Severen, qui prend racine dans les références et les résonnances partagées entre les travaux de deux pratiques contemporaines mises en présence de l’histoire. Alors que L’histoire, par ailleurs se fonde sur limpression que lon a du(...)
Vitrines
Cara Rachele, chercheure en résidence 2016, présente ses recherches: Cette conférence se penche sur l’explosion de dessins détaillés produits pendant la Renaissance. Elle établit le lien entre l’émergence, au XVIe siècle, du détail devenu un canon du dessin et l’évocation de l’antique matériel. L’évolution organique de la façon de dessiner les détails transparaît dans(...)
11 août 2016, 18h
Séminaire de chercheur en résidence : Cara Rachele
Actions:
Description:
Cara Rachele, chercheure en résidence 2016, présente ses recherches: Cette conférence se penche sur l’explosion de dessins détaillés produits pendant la Renaissance. Elle établit le lien entre l’émergence, au XVIe siècle, du détail devenu un canon du dessin et l’évocation de l’antique matériel. L’évolution organique de la façon de dessiner les détails transparaît dans(...)
Sous-série
CI001.S2.D5
Description:
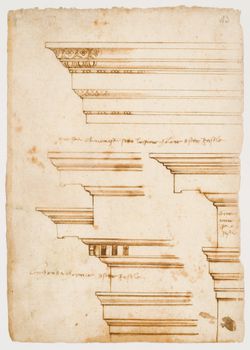
Charles Rohault de Fleury was architect for the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle from 1833 to 1862. His work for the Muséum is represented in the CCA collection by a diverse group of prints and drawings. In addition to documenting his built and unbuilt projects, the inclusion of prints and drawings of museum and zoo buildings by other architects record, if only partially, the resources available to Charles in designing his buildings. This reference material provides insight into the influences on Charles' work as well as the nature of the design process itself. His built works, with the exception of the 1854 addition to the greenhouses, are illustrated in a book of prints with a brief accompanying text - "Muséum d'histoire naturelle: serres chaudes, galeries de minéralogie, etc. etc." (published 1837) (DR1974:0002:004:001; a second copy is held by the CCA library) (1). While prints are included for the Galerie de minéralogie et de géologie, the monkey house and the reservoirs, the majority of the prints are of the greenhouses (serres chaudes) begun 1833 (2). Known for their technological innovations in iron construction, these greenhouses utilized the first multi-storey load-bearing cast-iron façades for the central pavilions as well as space frame roof structures and prefabricated parts. This structural system is well documented in the prints in the CCA collection. The design was apparently inspired by the English greenhouses - a plate of which are included in the book - that Charles saw on a tour of England. The use of prestressed beams and curved roofs in the lateral wings attest to this influence. Charles' greenhouses, in turn, influenced the design of other greenhouses in Europe especially those at the Jardins Botanique in Liège and Ghent, Belgium (3). Although Joseph Paxton saw the greenhouses in 1833, it is unclear if they had an impact on the design of the Crystal Palace constructed 1850-1851 (4). The innovations of Charles' greenhouses continued to be acknowledged into the 20th century. Giedion in "Space, Time and Architecture", while erroneously attributing them to Rouhault (5)(6), refers to the greenhouses as "the prototype of all large iron-framed conservatories" (7). In addition to the greenhouses for the Muséum, the CCA collection includes three proposals (dated 1841) for a private greenhouse designed by Charles Rohault de Fleury (DR1974:0002:002:008 - DR1974:0002:002:013). The designs utilize the same curved roofs as the wings of the greenhouses at the Muséum combined with classically detailed stonework. An different aspect of Charles' work for the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle is represented in the album of unexecuted proposals -the only design drawings for the Muséum in the collection - for a Galerie de zoologie (DR1974:0002:024:001-079). Building on the typology of his earlier classical Galerie de minéralogie et de géologie (constructed 1833 -1841), the proposals, which date from between 1838 and 1862, illustrate a gradual enrichment of Charles' classical architectural vocabulary (8). They vary in their spatial configurations and façade treatments ranging from austere colonnaded designs with little ornament to more elaborate ones with richly encrusted facades, complex rooflines and more dramatic interior spaces characteristic of the Second Empire. The majority of the proposals consist of preliminary drawings illustrating the essential formal, spatial and ornamental aspects of the building. One proposal, dated January 1846, is substantially more developed than the others; in addition to general plans, sections and elevations, more detailed drawings are included for the layout of spaces, the elaboration of the facades, the configuration of the structure and even the designs for the specimen display cases. It is also worth noting that this album includes several plans outlining Rohault de Fleury's ideas for the overall development of the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. In 1846, an album of prints of the Museo di fiscia e storia naturelle in Florence (DR1974:0002:005:001-018) was presented to Charles by the Grand Duke of Tuscany in response to his request for tracings of that building. These prints were probably used as reference material for the design of the new Galerie de zoologie described above. The portfolio of record drawings (ca. 1862) of the zoos in Antwerp, Brussels, Marseille and Amsterdam (DR1974:0002:018:001-027) is probably a dummy for a publication on zoological gardens as well as background documentation for the renovation and expansion of the zoo at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle in Paris. Both drawings of the facilities for the animals and visitors and general plans of the zoological gardens are included. The Paris zoo project was apparently never undertaken. (1) These prints were reused in the "Oeuvre de C. Rohault de Fleury, architecte" (published 1884) (DR1974:0002:029:001-044). (2) Rohault de Fleury's greenhouses were destroyed in the Prussian bombardments of 1870. The greenhouses, which now stand in their place, are similar in layout and appearance to the original design, but their structural system is different. (3) John Hix, 'The Glass House' (Cambridge, Mass.: The MIT Press, 1981), p. 115. (4) Ibid., p. 115. (5) This error has been repeated by other authors including Henry-Russell Hitchcock, 'Architecture: Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries' (Baltimore, Maryland: Penguin Books, 1968), p. 120. (6) Leonardo Benevolo, 'History of Modern Architecture' Volume 1: The tradition of modern architecture (Cambridge, Mass.: The M.I.T. Press, 1971), p. 22. (7) Sigfried Giedion, 'Space, Time and Architecture; the growth of a new tradition' (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1941), p. 181. (8) Barry Bergdoll, "Charles Rohault de Fleury: Part two: Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle and Studies on analogous Constructions in Europe", 'CCA Research Report", n.d., p. 1.
[1837-ca. 1862]
Muséum nationale d'histoire naturelle
CI001.S2.D5
Description:
Charles Rohault de Fleury was architect for the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle from 1833 to 1862. His work for the Muséum is represented in the CCA collection by a diverse group of prints and drawings. In addition to documenting his built and unbuilt projects, the inclusion of prints and drawings of museum and zoo buildings by other architects record, if only partially, the resources available to Charles in designing his buildings. This reference material provides insight into the influences on Charles' work as well as the nature of the design process itself. His built works, with the exception of the 1854 addition to the greenhouses, are illustrated in a book of prints with a brief accompanying text - "Muséum d'histoire naturelle: serres chaudes, galeries de minéralogie, etc. etc." (published 1837) (DR1974:0002:004:001; a second copy is held by the CCA library) (1). While prints are included for the Galerie de minéralogie et de géologie, the monkey house and the reservoirs, the majority of the prints are of the greenhouses (serres chaudes) begun 1833 (2). Known for their technological innovations in iron construction, these greenhouses utilized the first multi-storey load-bearing cast-iron façades for the central pavilions as well as space frame roof structures and prefabricated parts. This structural system is well documented in the prints in the CCA collection. The design was apparently inspired by the English greenhouses - a plate of which are included in the book - that Charles saw on a tour of England. The use of prestressed beams and curved roofs in the lateral wings attest to this influence. Charles' greenhouses, in turn, influenced the design of other greenhouses in Europe especially those at the Jardins Botanique in Liège and Ghent, Belgium (3). Although Joseph Paxton saw the greenhouses in 1833, it is unclear if they had an impact on the design of the Crystal Palace constructed 1850-1851 (4). The innovations of Charles' greenhouses continued to be acknowledged into the 20th century. Giedion in "Space, Time and Architecture", while erroneously attributing them to Rouhault (5)(6), refers to the greenhouses as "the prototype of all large iron-framed conservatories" (7). In addition to the greenhouses for the Muséum, the CCA collection includes three proposals (dated 1841) for a private greenhouse designed by Charles Rohault de Fleury (DR1974:0002:002:008 - DR1974:0002:002:013). The designs utilize the same curved roofs as the wings of the greenhouses at the Muséum combined with classically detailed stonework. An different aspect of Charles' work for the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle is represented in the album of unexecuted proposals -the only design drawings for the Muséum in the collection - for a Galerie de zoologie (DR1974:0002:024:001-079). Building on the typology of his earlier classical Galerie de minéralogie et de géologie (constructed 1833 -1841), the proposals, which date from between 1838 and 1862, illustrate a gradual enrichment of Charles' classical architectural vocabulary (8). They vary in their spatial configurations and façade treatments ranging from austere colonnaded designs with little ornament to more elaborate ones with richly encrusted facades, complex rooflines and more dramatic interior spaces characteristic of the Second Empire. The majority of the proposals consist of preliminary drawings illustrating the essential formal, spatial and ornamental aspects of the building. One proposal, dated January 1846, is substantially more developed than the others; in addition to general plans, sections and elevations, more detailed drawings are included for the layout of spaces, the elaboration of the facades, the configuration of the structure and even the designs for the specimen display cases. It is also worth noting that this album includes several plans outlining Rohault de Fleury's ideas for the overall development of the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. In 1846, an album of prints of the Museo di fiscia e storia naturelle in Florence (DR1974:0002:005:001-018) was presented to Charles by the Grand Duke of Tuscany in response to his request for tracings of that building. These prints were probably used as reference material for the design of the new Galerie de zoologie described above. The portfolio of record drawings (ca. 1862) of the zoos in Antwerp, Brussels, Marseille and Amsterdam (DR1974:0002:018:001-027) is probably a dummy for a publication on zoological gardens as well as background documentation for the renovation and expansion of the zoo at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle in Paris. Both drawings of the facilities for the animals and visitors and general plans of the zoological gardens are included. The Paris zoo project was apparently never undertaken. (1) These prints were reused in the "Oeuvre de C. Rohault de Fleury, architecte" (published 1884) (DR1974:0002:029:001-044). (2) Rohault de Fleury's greenhouses were destroyed in the Prussian bombardments of 1870. The greenhouses, which now stand in their place, are similar in layout and appearance to the original design, but their structural system is different. (3) John Hix, 'The Glass House' (Cambridge, Mass.: The MIT Press, 1981), p. 115. (4) Ibid., p. 115. (5) This error has been repeated by other authors including Henry-Russell Hitchcock, 'Architecture: Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries' (Baltimore, Maryland: Penguin Books, 1968), p. 120. (6) Leonardo Benevolo, 'History of Modern Architecture' Volume 1: The tradition of modern architecture (Cambridge, Mass.: The M.I.T. Press, 1971), p. 22. (7) Sigfried Giedion, 'Space, Time and Architecture; the growth of a new tradition' (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1941), p. 181. (8) Barry Bergdoll, "Charles Rohault de Fleury: Part two: Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle and Studies on analogous Constructions in Europe", 'CCA Research Report", n.d., p. 1.
File 5
[1837-ca. 1862]
recherche
Thème : Le phénomène baroque au-delà de Rome : Mark Dorrian, Département d’architecture, Université d’Édimbourg, Édimbourg, Royaume-Uni Sujet : Baroque Deformation Martina Frank, Département d’histoire, Université d’Udine, Udine, Italie Sujet : Luca Danesi et le baroque vénitien Indra McEwen, École nationale de théâtre du Canada, Montréal, Canada Sujet : The State of(...)
janvier 2000 au août 2000
Chercheurs en résidence 1999–2000
Actions:
Description:
Thème : Le phénomène baroque au-delà de Rome : Mark Dorrian, Département d’architecture, Université d’Édimbourg, Édimbourg, Royaume-Uni Sujet : Baroque Deformation Martina Frank, Département d’histoire, Université d’Udine, Udine, Italie Sujet : Luca Danesi et le baroque vénitien Indra McEwen, École nationale de théâtre du Canada, Montréal, Canada Sujet : The State of(...)
recherche
janvier 2000 au
août 2000
Penelope Dean, chercheure en résidence en 2011, examine les formes de l’histoire de l’architecture et la conception qui ont dominé pendant le XXe siècle et analyse un monde dans lequel il semble que le choix lui-même n’est imaginable que par la saturation préalable et omniprésente du design. Cliquez ici pour lévénement Facebook.
Maison Shaughnessy
21 juillet 2011 , 18h
Séminaire de chercheur en résidence : Penelope Dean
Actions:
Description:
Penelope Dean, chercheure en résidence en 2011, examine les formes de l’histoire de l’architecture et la conception qui ont dominé pendant le XXe siècle et analyse un monde dans lequel il semble que le choix lui-même n’est imaginable que par la saturation préalable et omniprésente du design. Cliquez ici pour lévénement Facebook.
Maison Shaughnessy
Images parlantes, un circuit
Tout au long d’un parcours d’interventions et d’installations en neuf segments à travers les espaces du CCA, Francesca Ammon, Davide Deriu, Reto Geiser, Sara Goldsmith, Catalina Mejía Moreno, Bas Princen, Mika Savela et Peter Sealy nous proposent de réfléchir aux relations essentielles et créatives qui unissent photographie et architecture. Au cours des dix huit(...)
Andrew W. Mellon Foundation, photographie, photographies, Francesca Ammon, Davide Deriu, Reto Geiser, Sara Goldsmith, Catalina Mejía Moreno, Bas Princen, Mika Savela, Peter Sealy
14 octobre 2017, 16h
Images parlantes, un circuit
Actions:
Description:
Tout au long d’un parcours d’interventions et d’installations en neuf segments à travers les espaces du CCA, Francesca Ammon, Davide Deriu, Reto Geiser, Sara Goldsmith, Catalina Mejía Moreno, Bas Princen, Mika Savela et Peter Sealy nous proposent de réfléchir aux relations essentielles et créatives qui unissent photographie et architecture. Au cours des dix huit(...)
Maristella Casciato : « Introducing Pierre Jeanneret—architect, designer, educator—in Chandigarh »
Le 18 novembre, Maristella Casciato, boursière et professeur d’histoire de l’architecture à l’École d’architecture « Aldo Rossi » de Cesenade, Université de Bologne, parle de la contribution essentielle de Pierre Jeanneret dans la construction de Chandigarh, en Inde. Ce séminaire présente « un autre » point de vue sur Pierre Jeanneret, cousin – moins connu – de Le Corbusier.
Théâtre Paul-Desmarais
Présentée en anglais Mot(s)-clé(s):
Maristella Casciato, Pierre Jeanneret
18 novembre 2010 , 18h
Maristella Casciato : « Introducing Pierre Jeanneret—architect, designer, educator—in Chandigarh »
Actions:
Description:
Le 18 novembre, Maristella Casciato, boursière et professeur d’histoire de l’architecture à l’École d’architecture « Aldo Rossi » de Cesenade, Université de Bologne, parle de la contribution essentielle de Pierre Jeanneret dans la construction de Chandigarh, en Inde. Ce séminaire présente « un autre » point de vue sur Pierre Jeanneret, cousin – moins connu – de Le Corbusier.
Théâtre Paul-Desmarais
Présentée en anglais Mot(s)-clé(s):
Maristella Casciato, Pierre Jeanneret
Les logements construits sur les toits des grandes tours par les résidents eux-mêmes font partie de l’histoire de Hong Kong depuis plus de cinquante ans. Ces structures vont de l’abri rudimentaire où se logent les plus démunis aux constructions à plusieurs étages dotées des commodités de la vie moderne. L’architecte Rufina Wu et le photographe Stefan Canham utilisent les(...)
Théâtre Paul Desmarais
3 mai 2012 , 19h
L'enseignement de... Hong Kong
Actions:
Description:
Les logements construits sur les toits des grandes tours par les résidents eux-mêmes font partie de l’histoire de Hong Kong depuis plus de cinquante ans. Ces structures vont de l’abri rudimentaire où se logent les plus démunis aux constructions à plusieurs étages dotées des commodités de la vie moderne. L’architecte Rufina Wu et le photographe Stefan Canham utilisent les(...)
Théâtre Paul Desmarais
archives
Niveau de description archivistique:
Collection
Futurecasting collection
CD048
Résumé:
This collection documents the activities of the “Futurecasting: Indigenous-led Architecture and Design in the Arctic” group formed by Jenni Hakovirta, Naomi Ratte, Nicole Luke, Magnus Antaris Tuolja, Andrea McIntosh, Robyn Adams, Berit Kristine Andersen Guvsám, Laila Susanna Kuhmunen, Johanna Minde, and Reanna Merasty. It contains materials related to the planning of seminars and workshops, and the creative process and projects created by its participants in 2022-2023 that were later presented in the Canadian Centre for Architecture’s exhibition and related publication “ᐊᖏᕐᕋᒧᑦ / Ruovttu Guvlui / Towards home” (2022-2023).
2008-2023
Futurecasting collection
Actions:
CD048
Résumé:
This collection documents the activities of the “Futurecasting: Indigenous-led Architecture and Design in the Arctic” group formed by Jenni Hakovirta, Naomi Ratte, Nicole Luke, Magnus Antaris Tuolja, Andrea McIntosh, Robyn Adams, Berit Kristine Andersen Guvsám, Laila Susanna Kuhmunen, Johanna Minde, and Reanna Merasty. It contains materials related to the planning of seminars and workshops, and the creative process and projects created by its participants in 2022-2023 that were later presented in the Canadian Centre for Architecture’s exhibition and related publication “ᐊᖏᕐᕋᒧᑦ / Ruovttu Guvlui / Towards home” (2022-2023).
archives
Niveau de description archivistique:
Collection
2008-2023
Quand Gordon Matta-Clark se procure les titres de propriété et la documentation d’une douzaine de petites parcelles non occupées à New York entre 1974 et 1977 (qui, en 1992, ont fait l’objet d’une exposition intitulée Reality Properties: Fake Estates), il n’a pas d’intention précise – autre que sa conviction suivant laquelle « l’existence de lots vacants et sous-utilisés(...)
Théâtre Paul-Desmarais
22 septembre 2016, 18h
Nicholas de Monchaux : Local Code
Actions:
Description:
Quand Gordon Matta-Clark se procure les titres de propriété et la documentation d’une douzaine de petites parcelles non occupées à New York entre 1974 et 1977 (qui, en 1992, ont fait l’objet d’une exposition intitulée Reality Properties: Fake Estates), il n’a pas d’intention précise – autre que sa conviction suivant laquelle « l’existence de lots vacants et sous-utilisés(...)
Théâtre Paul-Desmarais