archives
Niveau de description archivistique:
Fonds
Fonds Jean Michaud
AP012
Résumé:
Le Fonds Jean Michaud est constitué autour de 5 projets étudiants, 79 projets professionnels, 6 projets non identifiés, 13 projets réalisés par d'autres architectes, ainsi que divers documents visuels et textuels. Les projets de l'architecte sont répartis en 42 projets résidentiels, 4 pour les loisirs et l'animation sociale, 9 éducatifs, 7 commerciaux et administratifs, 3 industriels et manufacturiers, 1 pour le transport routier, 9 gouvernementales, 1 médical, 2 religieux et 1 projet d'aménagement urbain. Ces projets sont principalement concentrés dans quatre régions du Québec. Il y en a 29 dans la région de Montréal (incluant Laval et Vaudreuil-Dorion; dont 17 à Montréal), 20 dans la région du Bas-Saint-Laurent et Gaspésie (11 à Rimouski), 12 en Montérégie (8 à Saint-Marc-sur-Richelieu) et 7 dans les Laurentides. Le fonds Jean Michaud comprend 1613 dessins, 959 reprographies, 271 documents photographiques, 43 documents graphiques, 1 maquette, ainsi que 2.805 m.l. de documents textuels. Ces documents ont été principalement produits entre 1950 et 1970.
1852, 1916, 1938-1981, surtout 1950-1974
Fonds Jean Michaud
Actions:
AP012
Résumé:
Le Fonds Jean Michaud est constitué autour de 5 projets étudiants, 79 projets professionnels, 6 projets non identifiés, 13 projets réalisés par d'autres architectes, ainsi que divers documents visuels et textuels. Les projets de l'architecte sont répartis en 42 projets résidentiels, 4 pour les loisirs et l'animation sociale, 9 éducatifs, 7 commerciaux et administratifs, 3 industriels et manufacturiers, 1 pour le transport routier, 9 gouvernementales, 1 médical, 2 religieux et 1 projet d'aménagement urbain. Ces projets sont principalement concentrés dans quatre régions du Québec. Il y en a 29 dans la région de Montréal (incluant Laval et Vaudreuil-Dorion; dont 17 à Montréal), 20 dans la région du Bas-Saint-Laurent et Gaspésie (11 à Rimouski), 12 en Montérégie (8 à Saint-Marc-sur-Richelieu) et 7 dans les Laurentides. Le fonds Jean Michaud comprend 1613 dessins, 959 reprographies, 271 documents photographiques, 43 documents graphiques, 1 maquette, ainsi que 2.805 m.l. de documents textuels. Ces documents ont été principalement produits entre 1950 et 1970.
archives
Niveau de description archivistique:
Fonds
1852, 1916, 1938-1981, surtout 1950-1974
À partir du travail d’architectes de renommée internationale, cetteexposition démontre la présence d’idées utopiques modernes qui auraient été rejetées au tournant de l’ère postmoderne. Selon Reinhold Martin, commissaire principal de l’exposition, presque toute la production architecturale des cinquante dernières années a été hantée par le « revenant » de l’utopie(...)
Salle octogonale
28 février 2008 au 25 mai 2008
Le revenant de l'utopie: Le postmodernisme revisité
Actions:
Description:
À partir du travail d’architectes de renommée internationale, cetteexposition démontre la présence d’idées utopiques modernes qui auraient été rejetées au tournant de l’ère postmoderne. Selon Reinhold Martin, commissaire principal de l’exposition, presque toute la production architecturale des cinquante dernières années a été hantée par le « revenant » de l’utopie(...)
Salle octogonale
Projet
AP075.S1.1992.PR01
Description:
Project series documents Cornelia Hahn Oberlander’s project for the landscape design for Library Square, the new central branch of the Vancouver’s public library on West Georgia Street. Oberlander worked on this project in 1992-1995 with architect Moshe Safdie and architectural firm Downs/Archambault & Patners. Oberlander landscape design included a roof garden, planned to be accessible by the public, and terraces with integral planting of cascading roses of the southeast edge of the building. She was also consulted for the landscape for the street-level spaces: “Along the streets bordering the site, Oberlander selected tulip trees, except on W. Georgia Street where the city required maples.” [1] The project was completed in 1995. The project series contains sketches, design development drawings, including planting plans, landscape plans for the green roof and the plaza, working drawings, such as site plans, planting plans, irrigation plans, landscape sections and elevations, and drawings of the building used as reference. The project is also recorded through textual records, such as concept notes by Oberlander, research material, specifications, including landscape specifications, correspondence, including correspondence with architects, client and contractors, contract, financial documents, documents for plan selection, and press and articles on the project. The project series also includes photographs of the construction and landscaping work, and photographs of the completed project. Source: [1] Herrington, Susan. Cornelia Hahn Oberlander: Making the Modern Landscape, University of Virginia Press, 2014, 304 pages. p. 176.
1989-2009
Library Square, Vancouver, British Columbia (1992-1995)
Actions:
AP075.S1.1992.PR01
Description:
Project series documents Cornelia Hahn Oberlander’s project for the landscape design for Library Square, the new central branch of the Vancouver’s public library on West Georgia Street. Oberlander worked on this project in 1992-1995 with architect Moshe Safdie and architectural firm Downs/Archambault & Patners. Oberlander landscape design included a roof garden, planned to be accessible by the public, and terraces with integral planting of cascading roses of the southeast edge of the building. She was also consulted for the landscape for the street-level spaces: “Along the streets bordering the site, Oberlander selected tulip trees, except on W. Georgia Street where the city required maples.” [1] The project was completed in 1995. The project series contains sketches, design development drawings, including planting plans, landscape plans for the green roof and the plaza, working drawings, such as site plans, planting plans, irrigation plans, landscape sections and elevations, and drawings of the building used as reference. The project is also recorded through textual records, such as concept notes by Oberlander, research material, specifications, including landscape specifications, correspondence, including correspondence with architects, client and contractors, contract, financial documents, documents for plan selection, and press and articles on the project. The project series also includes photographs of the construction and landscaping work, and photographs of the completed project. Source: [1] Herrington, Susan. Cornelia Hahn Oberlander: Making the Modern Landscape, University of Virginia Press, 2014, 304 pages. p. 176.
Project
1989-2009
ARCH252733
Description:
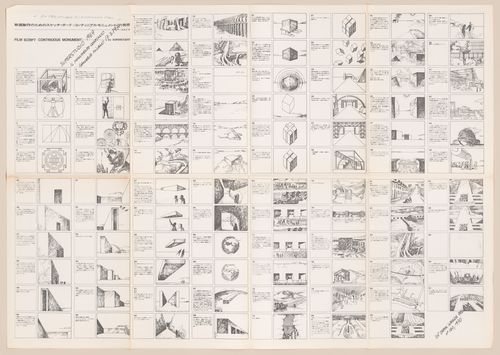
Full original title “Storyboard for a film for an American television company, MCW”), composed of a series of drawings that describe the many ways humans have applied order to their environment, the different monuments that have resulted—from Stonehenge to modern expressways—and a story of the discovery of the Continuous Monument, a single architectural model for the total urbanization of the world. Project led by founding members of Superstudio, without the direct involvement of Alessandro Poli.
1969-1971
Storyboard for audio-slideshow "The Continuous Monument"
Actions:
ARCH252733
Description:
Full original title “Storyboard for a film for an American television company, MCW”), composed of a series of drawings that describe the many ways humans have applied order to their environment, the different monuments that have resulted—from Stonehenge to modern expressways—and a story of the discovery of the Continuous Monument, a single architectural model for the total urbanization of the world. Project led by founding members of Superstudio, without the direct involvement of Alessandro Poli.
Projet
AP075.S1.1997.PR02
Description:
Project series documents Cornelia Hahn Oberlander's landscape project for the Waterfall Building on West 2nd Avenue, near the entrance of Granville Island, in Vancouver, British Columbia. Oberlander worked on this project in 1998-2001 with architect Arthur Erickson and architectural firm Nick Milkovich Architects, who designed the building. The building consists in five separated structures to accomodate studios spaces as well as split-level residences. It also included a courtyard and roof gardens on all five building structures for which Oberlander was responsible of the design. The courtyard, formed by in the roof of the underground parking space, consists "a simple tapestry of pavers, ground cover, trees and a small reflecting basin [...]." [1] The roofs garden included planting of white roses at the edge of the building and ornemental grass. The rooftops serve as communal patio for the residents and was accesible to the public. The project was completed in 2001. The Waterfall Building was the last project Oberlander realized in collaboration with Arthur Erickson. The project series includes sketches, design development drawings, including planting plans for the courtyard and the rooftops, working drawings, such as landscape plans for the courtyard and planting plans. The drawings in this series also includes drawings of the building used as reference. The project is also documented through research material for the project, specifications, plant lists, correspondence, including correspondence with architects and client, meeting notes, reports, financial document, a promotional poster on the project, and photographs of the landscaping work and plant selection. Source: [1] Herrington, Susan. Cornelia Hahn Oberlander: Making the Modern Landscape, University of Virginia Press, 2014, 304 pages. p. 142.
1997-2001
The Waterfall Building, Vancouver, British Columbia (1997)
Actions:
AP075.S1.1997.PR02
Description:
Project series documents Cornelia Hahn Oberlander's landscape project for the Waterfall Building on West 2nd Avenue, near the entrance of Granville Island, in Vancouver, British Columbia. Oberlander worked on this project in 1998-2001 with architect Arthur Erickson and architectural firm Nick Milkovich Architects, who designed the building. The building consists in five separated structures to accomodate studios spaces as well as split-level residences. It also included a courtyard and roof gardens on all five building structures for which Oberlander was responsible of the design. The courtyard, formed by in the roof of the underground parking space, consists "a simple tapestry of pavers, ground cover, trees and a small reflecting basin [...]." [1] The roofs garden included planting of white roses at the edge of the building and ornemental grass. The rooftops serve as communal patio for the residents and was accesible to the public. The project was completed in 2001. The Waterfall Building was the last project Oberlander realized in collaboration with Arthur Erickson. The project series includes sketches, design development drawings, including planting plans for the courtyard and the rooftops, working drawings, such as landscape plans for the courtyard and planting plans. The drawings in this series also includes drawings of the building used as reference. The project is also documented through research material for the project, specifications, plant lists, correspondence, including correspondence with architects and client, meeting notes, reports, financial document, a promotional poster on the project, and photographs of the landscaping work and plant selection. Source: [1] Herrington, Susan. Cornelia Hahn Oberlander: Making the Modern Landscape, University of Virginia Press, 2014, 304 pages. p. 142.
Project
1997-2001
Projet
AP075.S1.2008.PR02
Description:
Project series documents Cornelia Hahn Oberlander's project for the Inuvik School, later known as East Three School, in Inuvik, Northwest Territories. The project consisted in the landscape design and a playground design for the new school replacing the Sir Alexander MacKenzie elementary school and the Samuel Herne Secondary School. Oberlander worked on this project from 2008 to 2012 with architects Pin/Taylor. During her design process, Oberlander consulted the teachers, parents, staff and students on ways to express their culture in the landscape design. She also had to adapt her design to the extreme climate of the region. Oberlander located the play court at the angle of the two buildings of the elementary school and the secondary school, to shelter it from the wind, and allowing small children to play outside. The plant selection was made by "harvesting local site and surrounding area for plant material" [1] and was also inspired by traditional cuisine. The project was completed in 2012. The project series also includes some documents related to a project possibly unrealized of the Jim Koe Park also in Inuvik, near the school. The project series contains design development drawings and working drawings, such as planting plans, irrigation plans, grading plans, landscape sections, and site plans. The drawings also includes sets of building plans used as reference. The project is also documented through correspondence, including with architects, suppliers, and consultants, specifications, scope of work, schematic design and design reports from architectural firm, minutes of meetings, and research material. Source: [1] Herrington, Susan. Cornelia Hahn Oberlander: Making the Modern Landscape, University of Virginia Press, 2014, 304 pages, p. 197.
1999-2014
Inuvik School, Inuvik, Northwest Territories (2008)
Actions:
AP075.S1.2008.PR02
Description:
Project series documents Cornelia Hahn Oberlander's project for the Inuvik School, later known as East Three School, in Inuvik, Northwest Territories. The project consisted in the landscape design and a playground design for the new school replacing the Sir Alexander MacKenzie elementary school and the Samuel Herne Secondary School. Oberlander worked on this project from 2008 to 2012 with architects Pin/Taylor. During her design process, Oberlander consulted the teachers, parents, staff and students on ways to express their culture in the landscape design. She also had to adapt her design to the extreme climate of the region. Oberlander located the play court at the angle of the two buildings of the elementary school and the secondary school, to shelter it from the wind, and allowing small children to play outside. The plant selection was made by "harvesting local site and surrounding area for plant material" [1] and was also inspired by traditional cuisine. The project was completed in 2012. The project series also includes some documents related to a project possibly unrealized of the Jim Koe Park also in Inuvik, near the school. The project series contains design development drawings and working drawings, such as planting plans, irrigation plans, grading plans, landscape sections, and site plans. The drawings also includes sets of building plans used as reference. The project is also documented through correspondence, including with architects, suppliers, and consultants, specifications, scope of work, schematic design and design reports from architectural firm, minutes of meetings, and research material. Source: [1] Herrington, Susan. Cornelia Hahn Oberlander: Making the Modern Landscape, University of Virginia Press, 2014, 304 pages, p. 197.
Project
1999-2014
Projet
AP075.S1.1965.PR01
Description:
This project series documents Cornelia Hahn Oberlander's landscape project for the outdoor playground of the Children's Creative Centre. The Centre was part of the Canadian Federal Pavilion built for the Universal and International Exposition of 1967 (Expo 67), located at the south end of Notre-Dame Island in Montréal. Oberlander worked on this project from 1965-1966. She based her design on children's spontaneous exploration, to encourage self-motivation and creative play. The playground included a rolling terrain, looping paths, a wobble walk made of short logs embeded in the ground, a canal, and "giant wooden building pieces and a rocking boat in water replaced static sculptures". [1] The playground included a sand beach-like area with drifwood and plants to be used as play props. At the centre of the playground was a grass mound with an interior cave and a high wooden platform only reachable by a commando rope. A forty-foot long circulating water channel was situated in the east section of the playground and included two small islands linked by bridges, but was narrow enough to allow children to jump over it. The project series contains sketches, preliminary landscape concept plans, site plans, general landscape plans at different stages of design development, several sections and detail drawings for the playground's equipment and installations, and presentation drawings, including perspective views. The project series also contains architectural, electrical, and structural drawings of the Pavilion, which were provided to Oberlander for reference. Also included are photographs of the playground, research material on playgrounds, and articles and publications on the project, including Oberlander's writings, and publications on Expo '67. Source: [1] Herrington, Susan. Cornelia Hahn Oberlander: Making the Modern Landscape, University of Virginia Press, 2014, 304 pages. p. 106.
1965-1971
Children's Creative Centre Playground, Canadian Federal Pavilion, Expo '67, Montréal, Québec (1965-1967)
Actions:
AP075.S1.1965.PR01
Description:
This project series documents Cornelia Hahn Oberlander's landscape project for the outdoor playground of the Children's Creative Centre. The Centre was part of the Canadian Federal Pavilion built for the Universal and International Exposition of 1967 (Expo 67), located at the south end of Notre-Dame Island in Montréal. Oberlander worked on this project from 1965-1966. She based her design on children's spontaneous exploration, to encourage self-motivation and creative play. The playground included a rolling terrain, looping paths, a wobble walk made of short logs embeded in the ground, a canal, and "giant wooden building pieces and a rocking boat in water replaced static sculptures". [1] The playground included a sand beach-like area with drifwood and plants to be used as play props. At the centre of the playground was a grass mound with an interior cave and a high wooden platform only reachable by a commando rope. A forty-foot long circulating water channel was situated in the east section of the playground and included two small islands linked by bridges, but was narrow enough to allow children to jump over it. The project series contains sketches, preliminary landscape concept plans, site plans, general landscape plans at different stages of design development, several sections and detail drawings for the playground's equipment and installations, and presentation drawings, including perspective views. The project series also contains architectural, electrical, and structural drawings of the Pavilion, which were provided to Oberlander for reference. Also included are photographs of the playground, research material on playgrounds, and articles and publications on the project, including Oberlander's writings, and publications on Expo '67. Source: [1] Herrington, Susan. Cornelia Hahn Oberlander: Making the Modern Landscape, University of Virginia Press, 2014, 304 pages. p. 106.
Project
1965-1971
Arturo Ortiz Struck décrit les frontières de la construction légale et autorisée dans le contexte de Mexico :« Afin de nous forger une opinion critique sur la production d’espace et d’architecture dans cet environnement, nous devrions commencer par deux principes fondamentaux. Le premier établit que les espaces reflètent qui nous sommes, et ils traduisent nos habitudes(...)
Théâtre Paul-Desmarais
10 mai 2012 , 19h
L'enseignement de... Mexico : Arturo Ortiz Struck
Actions:
Description:
Arturo Ortiz Struck décrit les frontières de la construction légale et autorisée dans le contexte de Mexico :« Afin de nous forger une opinion critique sur la production d’espace et d’architecture dans cet environnement, nous devrions commencer par deux principes fondamentaux. Le premier établit que les espaces reflètent qui nous sommes, et ils traduisent nos habitudes(...)
Théâtre Paul-Desmarais
photographies
DR2012:0012:083:001
Description:
Ring binder containing slides, including those related to the following projects: - Modern art (9 slides); - Fuller dome at McGill University 1956 (4 slides); - Le rapport Charney 1972 (8 slides); - Architectural models, drawings and photographs, including works by John M. Johansen (26 slides); - Architectural models, drawings and photographs of école Notre-Dame des Laurentides, by Melvin Charney 1965-1966 (34 slides); - Une histoire 1973-1975 (134 slides, 10 appear to be duplicates); - Maisons de la rue Sherbrooke 1976 (40 slides, 13 appear to be duplicates); - Fragments series (35 slides including: Wall facade (18 slides), Maison de Rivière-des-Prairies (9 slides) and Garage Lennoxville (8 slides); - Painted photographs series: The house in St. Bonaventure 1978 (10 slides).
1956-1980, predominant 1965-1979
Slides of Melvin Charney's artworks
Actions:
DR2012:0012:083:001
Description:
Ring binder containing slides, including those related to the following projects: - Modern art (9 slides); - Fuller dome at McGill University 1956 (4 slides); - Le rapport Charney 1972 (8 slides); - Architectural models, drawings and photographs, including works by John M. Johansen (26 slides); - Architectural models, drawings and photographs of école Notre-Dame des Laurentides, by Melvin Charney 1965-1966 (34 slides); - Une histoire 1973-1975 (134 slides, 10 appear to be duplicates); - Maisons de la rue Sherbrooke 1976 (40 slides, 13 appear to be duplicates); - Fragments series (35 slides including: Wall facade (18 slides), Maison de Rivière-des-Prairies (9 slides) and Garage Lennoxville (8 slides); - Painted photographs series: The house in St. Bonaventure 1978 (10 slides).
photographies
1956-1980, predominant 1965-1979
Elevation of a palace façade
DR1970:0003
Description:
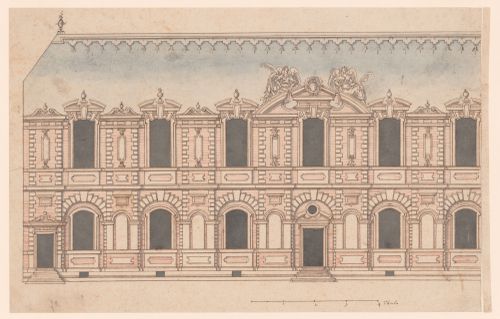
This drawing shows an exterior of a residential building. The artist uses color to suggest the materials used in construction; blue-grey for the pitched slate roof, brown for masonry details and architectural sculpture, and red striations for brickwork. This combination of materials was common in early modern France, where a play on color and materiality enlivened the façades of well-known royal edifices including the chateaux of Fontainebleau and Saint-Germain-en-Laye. As with the construction technique that interwove stone with brick, the architectural style depicted in the drawing combines traditional French ideas about building with classicizing elements imported to France via Italian artists and architects as well as through printed translations of Vitruvius’s 'De architectura' and Sebastiano Serlio’s architectural treatise. The inclusion of masonry rustication and the decorative urns that punctuate the roofline suggest a knowledge of classicizing trends in architectural ornament and a familiarity with the œuvre of artists working in the circle of the first and second Écoles de Fontainebleau. The structure’s elongated form suggests a gallery and the organization of the façade borrows the combination of slightly protruding vertical bays and long horizontal registers that characterizes Pierre Lescot’s wing of the Louvre, a project that would have been well-known in court circles in the latter half of the sixteenth century. Similarly, the two winged allegorical figures flanking the central pediment are reminiscent of Jean Goujon’s sculptural additions to the Lescot wing. In the Canadian Centre for Architecture’s drawing both figures hold palms, but the artist omitted any further identifying attributes, perhaps – along with the empty niches – as an invitation for the patron to imagine his or her own thematic program for the project.
first quarter of the 16th century
Elevation of a palace façade
Actions:
DR1970:0003
Description:
This drawing shows an exterior of a residential building. The artist uses color to suggest the materials used in construction; blue-grey for the pitched slate roof, brown for masonry details and architectural sculpture, and red striations for brickwork. This combination of materials was common in early modern France, where a play on color and materiality enlivened the façades of well-known royal edifices including the chateaux of Fontainebleau and Saint-Germain-en-Laye. As with the construction technique that interwove stone with brick, the architectural style depicted in the drawing combines traditional French ideas about building with classicizing elements imported to France via Italian artists and architects as well as through printed translations of Vitruvius’s 'De architectura' and Sebastiano Serlio’s architectural treatise. The inclusion of masonry rustication and the decorative urns that punctuate the roofline suggest a knowledge of classicizing trends in architectural ornament and a familiarity with the œuvre of artists working in the circle of the first and second Écoles de Fontainebleau. The structure’s elongated form suggests a gallery and the organization of the façade borrows the combination of slightly protruding vertical bays and long horizontal registers that characterizes Pierre Lescot’s wing of the Louvre, a project that would have been well-known in court circles in the latter half of the sixteenth century. Similarly, the two winged allegorical figures flanking the central pediment are reminiscent of Jean Goujon’s sculptural additions to the Lescot wing. In the Canadian Centre for Architecture’s drawing both figures hold palms, but the artist omitted any further identifying attributes, perhaps – along with the empty niches – as an invitation for the patron to imagine his or her own thematic program for the project.