archives
Niveau de description archivistique:
Fonds
AP192
Résumé:
The Morphosis Hypo Alpe-Adria Center project records, 1996 – 2016, consist of over 14,000 born-digital files that document the design and construction of the Austrian Hypo Alpe-Adria Bank group’s headquarters in Klagenfurt, Austria. Series 1, Competition and design, includes files showing early conceptualization of the project through the final design documentation. Series 2, Construction documentation, largely contains drawings and photographs which demonstrate the progress of the project in the built environment over time. Formats chiefly include CAD files (PowerCAD, PowerDraw, Microstation, DXF, AutoCAD, PLT), 3D models (Form*Z, STL), images, and text.
1996 - 2016
Documents d’archives de Morphosis pour le projet Centre Hypo Alpe-Adria
Actions:
AP192
Résumé:
The Morphosis Hypo Alpe-Adria Center project records, 1996 – 2016, consist of over 14,000 born-digital files that document the design and construction of the Austrian Hypo Alpe-Adria Bank group’s headquarters in Klagenfurt, Austria. Series 1, Competition and design, includes files showing early conceptualization of the project through the final design documentation. Series 2, Construction documentation, largely contains drawings and photographs which demonstrate the progress of the project in the built environment over time. Formats chiefly include CAD files (PowerCAD, PowerDraw, Microstation, DXF, AutoCAD, PLT), 3D models (Form*Z, STL), images, and text.
archives
Niveau de description archivistique:
Fonds
1996 - 2016
Projet
AP178.S1.2002.PR05
Description:
This project series documents the Parque de Vidago in Vidago, Portugal. While the records were held in the office’s archives this project was assigned the number 49/00. The office assigned the dates 2002-2010 to this project. This project consisted of extensive modifications to the spa resort Parque de Vidago Palace Hotel for owner VMPS - Águas & Turismo, S.A, part of Unicer (now Super Bock Group). The Palace Hotel and its surrounding nature park were originally proposed by King Carlos I at the beginning of the 20th century in order to create a luxurious resort around the famous Vidago mineral springs. In 2006, the resort was temporarily closed for the work to begin. For Siza, this primarily consisted of the construction of a new thermal spa, the conversion of rural buildings into vacation homes, and the building of a new clubhouse for the golf course. These three aspects of the project were divided as three subprojects by the office and have been arranged under AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS1, AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS2 and AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS3, respectively. While the spa and clubhouse were both built, the vacation homes were not realized. The resort reopened in 2010. Several smaller buildings were also realized as part of this project including the Fonte Salus (spring), the Fonte de Vidago (spring) and the Portaria (gatehouse). Materials for these three building are arranged in AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS1. Also included were several buildings that were not realized such as the Academia de golfe and the Edifício da manutenção (arranged in AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS3), and the Espaço Serralves (arranged in AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS1). This project was realized in tandem with another similar project by Siza, the Parque de Pedras Salgadas (AP178.S1.2002.PR06), also owned by Unicer. For this reason, the materials for both projects are mixed together. Files in this project series that contain materials for the Pedras Salgadas project have been identified at the file level.
2002-2012
Parque de Vidago [Vidago Palace], Vidago, Portugal (2002-2010)
Actions:
AP178.S1.2002.PR05
Description:
This project series documents the Parque de Vidago in Vidago, Portugal. While the records were held in the office’s archives this project was assigned the number 49/00. The office assigned the dates 2002-2010 to this project. This project consisted of extensive modifications to the spa resort Parque de Vidago Palace Hotel for owner VMPS - Águas & Turismo, S.A, part of Unicer (now Super Bock Group). The Palace Hotel and its surrounding nature park were originally proposed by King Carlos I at the beginning of the 20th century in order to create a luxurious resort around the famous Vidago mineral springs. In 2006, the resort was temporarily closed for the work to begin. For Siza, this primarily consisted of the construction of a new thermal spa, the conversion of rural buildings into vacation homes, and the building of a new clubhouse for the golf course. These three aspects of the project were divided as three subprojects by the office and have been arranged under AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS1, AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS2 and AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS3, respectively. While the spa and clubhouse were both built, the vacation homes were not realized. The resort reopened in 2010. Several smaller buildings were also realized as part of this project including the Fonte Salus (spring), the Fonte de Vidago (spring) and the Portaria (gatehouse). Materials for these three building are arranged in AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS1. Also included were several buildings that were not realized such as the Academia de golfe and the Edifício da manutenção (arranged in AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS3), and the Espaço Serralves (arranged in AP178.S1.2002.PR05.SS1). This project was realized in tandem with another similar project by Siza, the Parque de Pedras Salgadas (AP178.S1.2002.PR06), also owned by Unicer. For this reason, the materials for both projects are mixed together. Files in this project series that contain materials for the Pedras Salgadas project have been identified at the file level.
Project
2002-2012
Projet
AP206.S1.1975.PR01
Description:
This project series documents Aditya Prakash's proposal for an alternative plan for Chandigarh, India, which came to be known as the Linear City. Prakash began developing and advocating for this idea around the early 1970s. The Linear City had two fundamental ideas at its core. The first was to raise the roadways in Chandigarh (or any future city) 10-12 feet from ground level. This, he proposed, would separate vehicular traffic from pedestrians, eliminating all the hazardous impacts of traffic on daily life. The large part of the drawings for this project show sector plans and city blocks with evenly dispersed roundabout roadways as major transit hubs, wrapping around but high above centres of pedestrian activity that included shops, markets and green spaces. The sale of the land below the roadways would pay for the upheaval. He also recommended building this city only a few sectors deep, but endlessly expanding it length-wise, with a raised canal along one side to provide an additional transpiration network and irrigation. The second fundamental idea of this city was the creation of self-sustaining sectors in the city plan, advocating that each neighbourhood should have the infrastructure to provide food and recycling for its residents. He fervently argued for the reimagination of modernist Chandigarh by incorporating sustainable, local traditions - the rural should exist in harmony with the urban. In opposition to Le Corbusier and Pierre Jeanneret, he believed areas for recycling, animal husbandry, and growing food should be incorporated into the fabric of the city.[1] This project is recorded largely through original drawings of city plans, perspectives and axonometric views detailing Prakash's new vision for the city. It seems that many of the perspectives were drawn by family friend Sandeep Virmani, after listening to Prakash's ideas.[2] The project is also recorded through photographs, negatives and slides showing plans and the project model. A small amount of notes and an article on the project are also included. [1]Vikramaditya Prakash, One Continuous Line: Art, Architecture and Urbanism of Aditya Prakash (Ahmedabad, India: Mapin Publishing Pvt. Ltd., 2019), 164-181. [2]Prakash, One Continuous Line, 169.
circa 1975-2003
Linear city, Chandigarh, India (circa 1975-1987)
Actions:
AP206.S1.1975.PR01
Description:
This project series documents Aditya Prakash's proposal for an alternative plan for Chandigarh, India, which came to be known as the Linear City. Prakash began developing and advocating for this idea around the early 1970s. The Linear City had two fundamental ideas at its core. The first was to raise the roadways in Chandigarh (or any future city) 10-12 feet from ground level. This, he proposed, would separate vehicular traffic from pedestrians, eliminating all the hazardous impacts of traffic on daily life. The large part of the drawings for this project show sector plans and city blocks with evenly dispersed roundabout roadways as major transit hubs, wrapping around but high above centres of pedestrian activity that included shops, markets and green spaces. The sale of the land below the roadways would pay for the upheaval. He also recommended building this city only a few sectors deep, but endlessly expanding it length-wise, with a raised canal along one side to provide an additional transpiration network and irrigation. The second fundamental idea of this city was the creation of self-sustaining sectors in the city plan, advocating that each neighbourhood should have the infrastructure to provide food and recycling for its residents. He fervently argued for the reimagination of modernist Chandigarh by incorporating sustainable, local traditions - the rural should exist in harmony with the urban. In opposition to Le Corbusier and Pierre Jeanneret, he believed areas for recycling, animal husbandry, and growing food should be incorporated into the fabric of the city.[1] This project is recorded largely through original drawings of city plans, perspectives and axonometric views detailing Prakash's new vision for the city. It seems that many of the perspectives were drawn by family friend Sandeep Virmani, after listening to Prakash's ideas.[2] The project is also recorded through photographs, negatives and slides showing plans and the project model. A small amount of notes and an article on the project are also included. [1]Vikramaditya Prakash, One Continuous Line: Art, Architecture and Urbanism of Aditya Prakash (Ahmedabad, India: Mapin Publishing Pvt. Ltd., 2019), 164-181. [2]Prakash, One Continuous Line, 169.
Project
circa 1975-2003
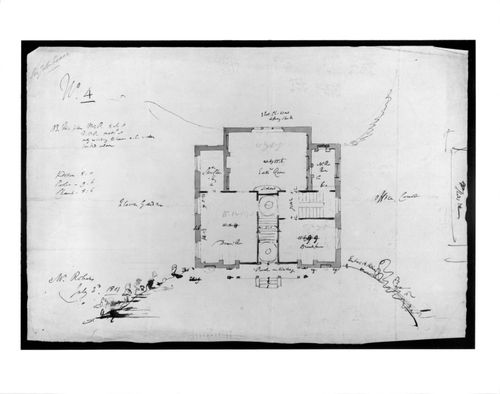
DR1983:0859
Description:
The plan of the building in pen and black ink and grey wash over graphite was executed by a draughtsman in Soane's office on the basis of pin-pricks transferring the design from another sheet. Soane's changes to this initial plan concern the addition of saucer domes in the main hall, and recesses in the "Eat. Room", which resulted in a change in the position of the fireplace in "Mr. Rs Room". The front porch was widened, presumably from the Doric version shown by Dorothy Stroud (1984, pl. 150) to one which includes "trelliage", showing a concern for setting this rural building in its landscape. This change, and its reflection in drawings in the Soane Museum (Drawer 4, set 4, Items 14-24) are discussed by Pierre du Prey (1986).
architecture
3 July 1801
Plan for a villa for Norwood Green, Middlesex
Actions:
DR1983:0859
Description:
The plan of the building in pen and black ink and grey wash over graphite was executed by a draughtsman in Soane's office on the basis of pin-pricks transferring the design from another sheet. Soane's changes to this initial plan concern the addition of saucer domes in the main hall, and recesses in the "Eat. Room", which resulted in a change in the position of the fireplace in "Mr. Rs Room". The front porch was widened, presumably from the Doric version shown by Dorothy Stroud (1984, pl. 150) to one which includes "trelliage", showing a concern for setting this rural building in its landscape. This change, and its reflection in drawings in the Soane Museum (Drawer 4, set 4, Items 14-24) are discussed by Pierre du Prey (1986).
architecture
Série(s)
AP193.S1
Description:
Series 1, Water Flux and Scrambled Flat, 2002-2010, documents the conception and evolution of a project that was originally a farm building and later became a geology and glaciology museum and research center focused on the Swiss Alps. The project was never realized. R&Sie(n) conceptualized Scrambled Flat as an experimental farm. The project goal was to reconcile European Union’s agricultural regulations, imposing a separation between animal and human living, to the community of Évolène traditional way of living, contiguously with animals, benefiting from the resources they offer. As conceived, Scrambled Flat creates an environment where fluidity between the existence of the animals and the humans is materialized. The size of the form is also adapted from a typical local rural house and exploits the heat of the animals and the insulation of the hay. For this project, R&Sie(n) approached the mayor of the community with the design proposition. The mayor then called for a competition, while also changing the program to an ecology museum and research center illustrating the local effects of global warming and the thawing of the Alps. R&Sie(n) won the competition with Water Flux, a reinterpretation of Scrambled Flat. The project was intended to uncover and exorcise the anxieties of ecological disaster, and the principle of flux related to seasonal change and, more broadly, climate change. The firm designed rooms that reproduce the geological and meteorological environment of the high mountains making it visible and experimental, offering refrigerated spaces for art installations and scientific demonstrations. The concept was also to build with the use of new technologies such as digital modelling, point scanning, and computer numerical control (CNC), combined with ancient local knowledge of knocking on trees to decide which specific pines have the best wood for construction. The building is designed to be constructed with local lamellar wood milled by nearby CNC. The resulting parts would be used for the structure, the insulation, the waterproofing and both the interior and exterior finishes. The design includes a grille wrapping the building, reproducing the profile of traditional houses and enclosure and making it possible to hold the snow inside a typo-morphological imprint. Therefore, the transformable envelope of the building reacts to the rhythm of the seasons. In the winter, the structure would appear like a solid cut-out of ice and snow, with cavities similar to those found in glaciers. In the summer, it would resemble piles of stones used in these areas to make borders. A small pool would collect rainwater and supply it to an interior artificial snowmaking system designed for the gallery. Transformation of the water is an integral part of the design. The records contain images of plans, sections, details for the structure of the façade, renderings, plans of the engineered structure, and photographs documenting the conception of the models with the CNC machinery. The Rhino 3D modelling files are also part of the records along with AutoCAD models and a video documenting the process. The records contain two physical models: a smaller polymer model at 1:20 scale representing the whole structure of the building, and a larger 1:1 latch wood fragment representing detail of the structure in its integrality.
2002-2010
Water Flux and Scrambled Flat
Actions:
AP193.S1
Description:
Series 1, Water Flux and Scrambled Flat, 2002-2010, documents the conception and evolution of a project that was originally a farm building and later became a geology and glaciology museum and research center focused on the Swiss Alps. The project was never realized. R&Sie(n) conceptualized Scrambled Flat as an experimental farm. The project goal was to reconcile European Union’s agricultural regulations, imposing a separation between animal and human living, to the community of Évolène traditional way of living, contiguously with animals, benefiting from the resources they offer. As conceived, Scrambled Flat creates an environment where fluidity between the existence of the animals and the humans is materialized. The size of the form is also adapted from a typical local rural house and exploits the heat of the animals and the insulation of the hay. For this project, R&Sie(n) approached the mayor of the community with the design proposition. The mayor then called for a competition, while also changing the program to an ecology museum and research center illustrating the local effects of global warming and the thawing of the Alps. R&Sie(n) won the competition with Water Flux, a reinterpretation of Scrambled Flat. The project was intended to uncover and exorcise the anxieties of ecological disaster, and the principle of flux related to seasonal change and, more broadly, climate change. The firm designed rooms that reproduce the geological and meteorological environment of the high mountains making it visible and experimental, offering refrigerated spaces for art installations and scientific demonstrations. The concept was also to build with the use of new technologies such as digital modelling, point scanning, and computer numerical control (CNC), combined with ancient local knowledge of knocking on trees to decide which specific pines have the best wood for construction. The building is designed to be constructed with local lamellar wood milled by nearby CNC. The resulting parts would be used for the structure, the insulation, the waterproofing and both the interior and exterior finishes. The design includes a grille wrapping the building, reproducing the profile of traditional houses and enclosure and making it possible to hold the snow inside a typo-morphological imprint. Therefore, the transformable envelope of the building reacts to the rhythm of the seasons. In the winter, the structure would appear like a solid cut-out of ice and snow, with cavities similar to those found in glaciers. In the summer, it would resemble piles of stones used in these areas to make borders. A small pool would collect rainwater and supply it to an interior artificial snowmaking system designed for the gallery. Transformation of the water is an integral part of the design. The records contain images of plans, sections, details for the structure of the façade, renderings, plans of the engineered structure, and photographs documenting the conception of the models with the CNC machinery. The Rhino 3D modelling files are also part of the records along with AutoCAD models and a video documenting the process. The records contain two physical models: a smaller polymer model at 1:20 scale representing the whole structure of the building, and a larger 1:1 latch wood fragment representing detail of the structure in its integrality.
Series
2002-2010
documents textuels
ARCH267991
Description:
Documents concern the following buildings in Chandigarh: the animal house and workshop at the Institute for Medical Research, the Institute for Medical Research (Sector 12), Saroop Krishan's house (Sector 8), various schools (nursery, primary and secondary), the Chandigarh Club, low-cost homes, and small office buildings. Texts also consider Pierre Jeanneret's furniture designs. Also includes: - "Social Sciences Research Journal," volume 4, number 2 (July 1979) concerning Chandigarh, India. - "An architect's plea to resolve the problems / of human settlement in South Asia / A design of composite organisation to prepare typical plans of hierarchy of human settlements in India and other parts of Suth [sic] Asia" by Jeet Malhotra, prepared for a symposium on human settlements with special reference to rural settlements in South Asia (March 18-21, 1976). - "A brief note on the conceptual man-made / environmental grid plan for Punjab / to avoid pollution of air, land, water / etc. - a preventative strategy" by Jeet Malhotra (n.d.). - "Architecture 2000 A.D. - Indian Context" by Jeet Malhotra, possibly prepared for the national convention of the Council of Architecture, New Delhi, which took place February 22-23, 1985.
Writings by Jeet Malhotra, predominantly pertaining to Chandigarh, with some concerning Talwara and Punjab, India
Actions:
ARCH267991
Description:
Documents concern the following buildings in Chandigarh: the animal house and workshop at the Institute for Medical Research, the Institute for Medical Research (Sector 12), Saroop Krishan's house (Sector 8), various schools (nursery, primary and secondary), the Chandigarh Club, low-cost homes, and small office buildings. Texts also consider Pierre Jeanneret's furniture designs. Also includes: - "Social Sciences Research Journal," volume 4, number 2 (July 1979) concerning Chandigarh, India. - "An architect's plea to resolve the problems / of human settlement in South Asia / A design of composite organisation to prepare typical plans of hierarchy of human settlements in India and other parts of Suth [sic] Asia" by Jeet Malhotra, prepared for a symposium on human settlements with special reference to rural settlements in South Asia (March 18-21, 1976). - "A brief note on the conceptual man-made / environmental grid plan for Punjab / to avoid pollution of air, land, water / etc. - a preventative strategy" by Jeet Malhotra (n.d.). - "Architecture 2000 A.D. - Indian Context" by Jeet Malhotra, possibly prepared for the national convention of the Council of Architecture, New Delhi, which took place February 22-23, 1985.
documents textuels
Sous-série
Domestic Commissions
CI001.S2.D2
Description:
Hubert and Charles Rohault de Fleury received domestic commissions for both urban housing -hôtel particuliers and apartment houses- and rural dwellings -châteaux, country houses and estates. Hubert also executed designs for furniture and garden pavilions. Hubert' work is characterized by restrained classical exteriors and luxurious Empire style interiors; both Charles' exteriors and interiors, especially those for Hôtels Sauvage and Soltykoff, reflect the exuberance of the Second Empire. The CCA albums include drawings from all stages of the design process but with an emphasis on design development drawings. Hubert's albums contain cost calculations and estimates, notes and letters. In general, the drawings by Charles are from a more developed phase of design than Hubert's; Hubert's commissions are more varied than Charles'. Charles' Hôtel Soltykoff (1854)(DR1974:0002:003:001-105) is exemplary of the Second Empire not only in its architectural language, programme and interior decoration, but also its use of mixed stone and iron construction. The album for Hôtel Soltykoff is one of the most comprehensive in the CCA collection. The drawings incorporate several phases of the design process from conceptual ideas to post-construction revisions. Numerous drawings for the structure and exterior ornamentation are included as well as drawings for the embellishment of the interior spaces. The interior drawings are especially interesting for evidence they provide of the palette of colours and ornamental motifs utilized in the Second Empire. Several prints (plates XIX - XXIII) in 'Oeuvre de C. Rohault de Fleury, architecte', which include general plans and elevations (few of which are included in the Hôtel Solytkoff album), are a useful complement to more specific drawings in the album. The Hôtel Sauvage (ca. 1862) album (DR1974:0002:006:001-024) - a set of 24 contract drawings- consists exclusively general plans, sections and elevations. This group of drawings give a good overall sense of both the interior and exterior. Hôtel Sauvage, like Hôtel Soltykoff is also typical of the Second Empire in style and programme. Château de Marcoussis (ca. 1861), for which a group of drawings were acquired in 1986, diverges somewhat in character from the other examples of Charles' domestic works represented in the CCA collection (DR1986:0379 - DR1986:0413). While most of the other houses are strictly classical in planning and design, for Château de Marcoussis, Charles adopted a more romantic asymmetrical château style design. The domestic commissions (1838-1856) in album, DR1974:0002:002:001-094, roughly fall into two categories. The first category consists of single residences - both town and country. The regimentation of plans and façades in the hôtel particular and country houses manifests the continued influence of Durand, yet Charles was also clearly affected by the Second Empire propensity for elaborate façade treatments with decoratively-shaped windows, complex mouldings and extensive rustication. The second category consists of urban apartment building with stores or occasionally offices on the ground floor, apartments, generally two per floor, above and often servants' rooms in the attic. These buildings are articulated in a restrained manner with mouldings, decorative ironwork and some stone ornament.
[between 1838 and 1861]
Domestic Commissions
CI001.S2.D2
Description:
Hubert and Charles Rohault de Fleury received domestic commissions for both urban housing -hôtel particuliers and apartment houses- and rural dwellings -châteaux, country houses and estates. Hubert also executed designs for furniture and garden pavilions. Hubert' work is characterized by restrained classical exteriors and luxurious Empire style interiors; both Charles' exteriors and interiors, especially those for Hôtels Sauvage and Soltykoff, reflect the exuberance of the Second Empire. The CCA albums include drawings from all stages of the design process but with an emphasis on design development drawings. Hubert's albums contain cost calculations and estimates, notes and letters. In general, the drawings by Charles are from a more developed phase of design than Hubert's; Hubert's commissions are more varied than Charles'. Charles' Hôtel Soltykoff (1854)(DR1974:0002:003:001-105) is exemplary of the Second Empire not only in its architectural language, programme and interior decoration, but also its use of mixed stone and iron construction. The album for Hôtel Soltykoff is one of the most comprehensive in the CCA collection. The drawings incorporate several phases of the design process from conceptual ideas to post-construction revisions. Numerous drawings for the structure and exterior ornamentation are included as well as drawings for the embellishment of the interior spaces. The interior drawings are especially interesting for evidence they provide of the palette of colours and ornamental motifs utilized in the Second Empire. Several prints (plates XIX - XXIII) in 'Oeuvre de C. Rohault de Fleury, architecte', which include general plans and elevations (few of which are included in the Hôtel Solytkoff album), are a useful complement to more specific drawings in the album. The Hôtel Sauvage (ca. 1862) album (DR1974:0002:006:001-024) - a set of 24 contract drawings- consists exclusively general plans, sections and elevations. This group of drawings give a good overall sense of both the interior and exterior. Hôtel Sauvage, like Hôtel Soltykoff is also typical of the Second Empire in style and programme. Château de Marcoussis (ca. 1861), for which a group of drawings were acquired in 1986, diverges somewhat in character from the other examples of Charles' domestic works represented in the CCA collection (DR1986:0379 - DR1986:0413). While most of the other houses are strictly classical in planning and design, for Château de Marcoussis, Charles adopted a more romantic asymmetrical château style design. The domestic commissions (1838-1856) in album, DR1974:0002:002:001-094, roughly fall into two categories. The first category consists of single residences - both town and country. The regimentation of plans and façades in the hôtel particular and country houses manifests the continued influence of Durand, yet Charles was also clearly affected by the Second Empire propensity for elaborate façade treatments with decoratively-shaped windows, complex mouldings and extensive rustication. The second category consists of urban apartment building with stores or occasionally offices on the ground floor, apartments, generally two per floor, above and often servants' rooms in the attic. These buildings are articulated in a restrained manner with mouldings, decorative ironwork and some stone ornament.
File 2
[between 1838 and 1861]
articles
Pèlerinage photographique
La vie des documents, la photographie en tant que projet, Stefano Graziani et Bas Princen, Guido Guidi, conversation, histoire orale
27 juin 2023
Pèlerinage photographique
Guido Guidi en conversation avec Stefano Graziani et Bas Princen
Actions:
Comme directeur des Bâtiments du Bade, un petit État du sud-ouest de l’Allemagne, Friedrich Weinbrenner (1766-1826) aura la chance peu commune de pouvoir créer à Karlsruhe, sa ville natale, l’un des ensembles architecturaux les plus homogènes qui soit. L’exposition met en lumière l’influence des réformes scientifiques et administratives sur l’architecture urbaine et(...)
Salles principales
31 janvier 1990 au 18 mars 1990
Friedrich Weinbrenner, l'architecte de Karlsruhe
Actions:
Description:
Comme directeur des Bâtiments du Bade, un petit État du sud-ouest de l’Allemagne, Friedrich Weinbrenner (1766-1826) aura la chance peu commune de pouvoir créer à Karlsruhe, sa ville natale, l’un des ensembles architecturaux les plus homogènes qui soit. L’exposition met en lumière l’influence des réformes scientifiques et administratives sur l’architecture urbaine et(...)
Salles principales
Sous-série
Domestic Commissions
CI001.S1.D2
Description:
Hubert and Charles Rohault de Fleury received domestic commissions for both urban housing -hôtel particuliers and apartment houses- and rural dwellings -châteaux, country houses and estates. Hubert also executed designs for furniture and garden pavilions. Hubert' work is characterized by restrained classical exteriors and luxurious Empire style interiors; both Charles' exteriors and interiors, especially those for Hôtels Sauvage and Soltykoff, reflect the exuberance of the Second Empire. The CCA albums include drawings from all stages of the design process but with an emphasis on design development drawings. Hubert's albums contain cost calculations and estimates, notes and letters. In general, the drawings by Charles are from a more developed phase of design than Hubert's; Hubert's commissions are more varied than Charles'. The austere classicism of Hubert's domestic work reflects the prevailing taste of the day and reveals the strong influence of his teacher, Jean Nicholas Louis Durand. The compostional effect of the houses' façades relies on the shape and rhythm of the fenestration and the geometric division by string courses and occasionally, pilasters. Columns are used infrequently as is decorative stonework. The plans are symmetrical and modular. This approach to design is especially evident in the series of proposals for a country house for comte Treilhard (DR1974:0002:034:001-082) and in a group of unidentified designs for houses (DR1974:0002:035:001-034), all of which illustrate an emphasis on plan in the design process and a distinct approach to the composition of the elevations, both derived from Durand. Hubert's domestic work was also influenced by Palladio (see especially DR1974:0002:038:001-029). The interiors and furniture designed by Hubert are typical of the Empire style (1). The drawings in the CCA collection illustrate the materials, palette and ornamental motifs of the period. The garden structures in Hubert's albums are more fanciful than his houses and are either Rustic, Chinoiserie or classical in style (2). His garden designs follow the contemporary French trend for "jardins anglais" with winding paths and naturalistic placement of the vegetation, sometimes in combination with more formal French gardens (3). One of the most comprehensively documented domestic project by Hubert is the Rohault de Fleury House (12-14 rue d'Aguesseau; 1824). The CCA collection contains an interesting series of preliminary drawings for alternate proposals for this house, a number of highly finished wash drawings (including the interior decorative scheme) for the final scheme (DR1974:0002:011:001-08) and several earlier (ca. 1806) proposals (DR1974:0002:035:001-034). The Domaine de la Vallée album (DR1974:0002:025:001-059) is notable for the range of subject matter included as well as for the insights into the character of a working country estate in the nineteenth century. The proposed modifications encompassed both functional (a bridge, a levee, granaries and stables) and aesthetic improvements, such as ornamental garden temples. The renovation of the house also exhibits both functional and aesthetic improvements. (1) Examples of Hubert's interiors and furniture can be found in albums, DR1974:0002:007:001-068, DR1974:0002:011:001-089, DR1974:0002:025:001-059, DR1974:0002:030:001-065 and DR1974:0002:035:001-034. (2) The best examples of his pavilions are found in album, DR1974:0002:038:001-029 with other examples in albums, DR1974:0002:025:001-059, DR1974:0002:030:001-065 and DR1974:0002:035:001-034. (3) Examples are found in albums, DR1974:0002:035:001-034 and DR1974:0002 :025:001-059. Also of note are drawings, DR1974:0002:007:007 and DR1974:0002:007:068.
1802-[1840]
Domestic Commissions
CI001.S1.D2
Description:
Hubert and Charles Rohault de Fleury received domestic commissions for both urban housing -hôtel particuliers and apartment houses- and rural dwellings -châteaux, country houses and estates. Hubert also executed designs for furniture and garden pavilions. Hubert' work is characterized by restrained classical exteriors and luxurious Empire style interiors; both Charles' exteriors and interiors, especially those for Hôtels Sauvage and Soltykoff, reflect the exuberance of the Second Empire. The CCA albums include drawings from all stages of the design process but with an emphasis on design development drawings. Hubert's albums contain cost calculations and estimates, notes and letters. In general, the drawings by Charles are from a more developed phase of design than Hubert's; Hubert's commissions are more varied than Charles'. The austere classicism of Hubert's domestic work reflects the prevailing taste of the day and reveals the strong influence of his teacher, Jean Nicholas Louis Durand. The compostional effect of the houses' façades relies on the shape and rhythm of the fenestration and the geometric division by string courses and occasionally, pilasters. Columns are used infrequently as is decorative stonework. The plans are symmetrical and modular. This approach to design is especially evident in the series of proposals for a country house for comte Treilhard (DR1974:0002:034:001-082) and in a group of unidentified designs for houses (DR1974:0002:035:001-034), all of which illustrate an emphasis on plan in the design process and a distinct approach to the composition of the elevations, both derived from Durand. Hubert's domestic work was also influenced by Palladio (see especially DR1974:0002:038:001-029). The interiors and furniture designed by Hubert are typical of the Empire style (1). The drawings in the CCA collection illustrate the materials, palette and ornamental motifs of the period. The garden structures in Hubert's albums are more fanciful than his houses and are either Rustic, Chinoiserie or classical in style (2). His garden designs follow the contemporary French trend for "jardins anglais" with winding paths and naturalistic placement of the vegetation, sometimes in combination with more formal French gardens (3). One of the most comprehensively documented domestic project by Hubert is the Rohault de Fleury House (12-14 rue d'Aguesseau; 1824). The CCA collection contains an interesting series of preliminary drawings for alternate proposals for this house, a number of highly finished wash drawings (including the interior decorative scheme) for the final scheme (DR1974:0002:011:001-08) and several earlier (ca. 1806) proposals (DR1974:0002:035:001-034). The Domaine de la Vallée album (DR1974:0002:025:001-059) is notable for the range of subject matter included as well as for the insights into the character of a working country estate in the nineteenth century. The proposed modifications encompassed both functional (a bridge, a levee, granaries and stables) and aesthetic improvements, such as ornamental garden temples. The renovation of the house also exhibits both functional and aesthetic improvements. (1) Examples of Hubert's interiors and furniture can be found in albums, DR1974:0002:007:001-068, DR1974:0002:011:001-089, DR1974:0002:025:001-059, DR1974:0002:030:001-065 and DR1974:0002:035:001-034. (2) The best examples of his pavilions are found in album, DR1974:0002:038:001-029 with other examples in albums, DR1974:0002:025:001-059, DR1974:0002:030:001-065 and DR1974:0002:035:001-034. (3) Examples are found in albums, DR1974:0002:035:001-034 and DR1974:0002 :025:001-059. Also of note are drawings, DR1974:0002:007:007 and DR1974:0002:007:068.
File 2
1802-[1840]